Fiberglass (Glass wool) is an insulating material made from fibers of glass arranged using a binder into a texture similar to wool. Glass wool and stone wool are produced from mineral fibers and are therefore often referred to as ‘mineral wools. Mineral wool is a general name for fiber materials that are formed by spinning or drawing molten minerals.
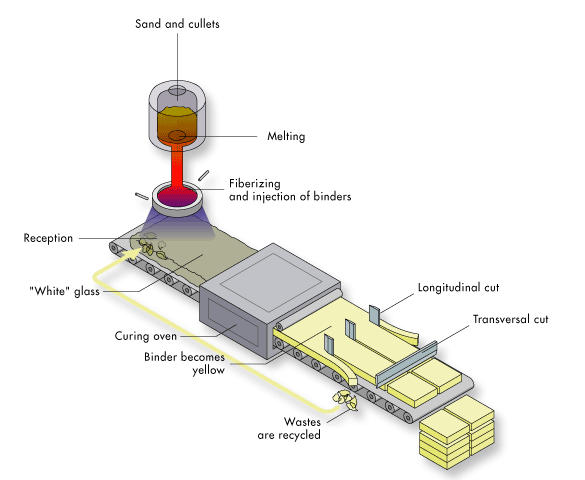
Glass wool is a furnace product of molten glass at a temperature of about 1450 °C. From the melted glass, fibers are spun. This process is based on spinning molten glass in high-speed spinning heads somewhat like the process used to produce cotton candy. During the spinning of the glass fibers, a binding agent is injected. Glass wool is then produced in rolls or in slabs, with different thermal and mechanical properties. It may also be produced as a material that can be sprayed or applied in place, on the surface to be insulated.
Applications
- Structural insulation
- Filtration and sound proofing
- loose fill material, blown into attics, or, together with an active binder sprayed on the underside of structures
- used for the insulation of walls, roofs and floors due to its versatility
- pipe insulation
Fiberglass Raw Materials
Natural minerals and manufactured chemicals are the main ingredients of fiberglass products. Silica sand, limestone and soda ash form the major components in the manufacture of glass wool. Other ingredients include: calcined alumina, nepheline syenite,feldspar, magnesite, borax and kaolin clay among others.
The purpose of silica sand is to act as a glass former while limestone and soda ash are used to lower the melting temperature. Other ingredients help in improving various properties in the fiberglass e.g borax is used to improve chemical resistance. Waste glass (cullet) is also used as a raw materials.

Manufacturing Process of Fiberglass